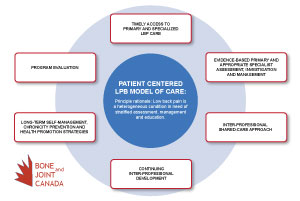
Skills and knowledge of a range of health professionals who share joint responsibility in an individual patient’s care
Patient management within a Shared Care Model is based on explicit individual patient goals, and includes the patient in planning and decision making
Requires clear definitions of roles and responsibilities of the inter-professional team (on-site, virtual or networked)
Requires consistent patient messaging and structured communication between providers regarding use of evidence based recommendations
Interprofessional relations in a Shared Care Model include:
- Appropriate, rapid, streamlined access to networked specialists, diagnostic and community based allied health services
- Networked specialists with a shared responsibility for patient care and provide joint provision of clinical services
- Communication on use of evidence-based treatment and referral guidelines
- Clear differentiation of roles and legal responsibilities between providers
- Collaborative professional education and training of health care providers
Interprofessional Communication associated with:
- Referral practices, eligibility criteria, standardized referral form
- Standardized consult note back to primary care on treatment recommendations
- Referral process to specialists and other providers to be made by the primary care provider (referral to spine surgeon is made by treating clinician)
- Return to activity/work recommendations
- Consistent messaging to the patient in a shared care model

Referral practices: ISAEC report form
Referral form to access the ISAEC program
![]()
Referral practices: Saskatchewan referral form
Referral form to access the SK program
![]()